INTERNET
The Internet is a massive
network of networks, a networking infrastructure. It connects millions of
computers together globally, forming a network in which any computer can
communicate with any other computer as long as they are both connected to the
Internet.
Each
Internet computer, called a host, is independent. Its operators can choose
which Internet services to use and which local services to make available to
the global Internet community. Remarkably, this anarchy by design works exceedingly
well. There are a variety of ways to access the Internet. Most online services
offer access to some Internet services. It is also possible to gain access
through a commercial Internet Service Provider (ISP).
INTraNET
An intranet is a private network (private network) that uses
Internet protocols (TCP / IP), to share confidential information within a
company or operating company to its employees. Sometimes, the term intranet
refers only to services that are visible, the company’s internal Web site. To
build an intranet, a network must have some components that build the Internet,
the Internet protocol (TCP / IP, IP address, and other protocols), the client
and the server. HTTP protocol and several other Internet protocols (FTP, POP3,
or SMTP) protocol is generally a component that is often used.
Generally, an intranet can be understood as a “personal version of
the Internet”, or as a version of the Internet that are owned by an
organization.
extraNET
A buzzword that refers to an
intranet that is partially accessible to authorized outsiders. Whereas an
intranet resides behind a firewall and is accessible only to people who are
members of the same company or organization, an extranet provides various
levels of accessibility to outsiders. You can access an extranet only if you
have a valid username and password, and your identity determines which parts of
the extranet you can view.
Extranets
are becoming a very popular means for business partners to exchange
information.
internetwork
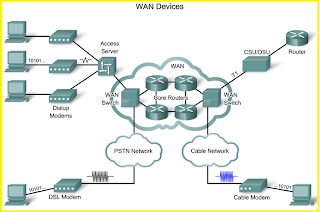
The
art and science of connecting individual local-area networks (LANs) to create
wide-area networks (WANs) , and connecting WANs to form even larger WANs.
Internetworking can be extremely complex because it generally involves
connecting networks that use different protocols. Internetworking is
accomplished with routers, bridges, and gateways.


